Earth Day 2017

“We don’t inherit the earth from our ancestors. We borrow it from our children.”
Chief Seattle

Save
Save
Nature and infrastructure are not independent of each other; on the contrary, nature is infrastructure. From protecting communities from flooding and excessive heat to improving air and water quality, nature is not only a critically important element of infrastructure but also a vital part of human and environmental health. When nature is used as an infrastructural system, it’s referred to as green infrastructure. 
Green infrastructure can be a highlight of regional and metropolitan planning, helping ensure communities have a safe, livable environment with clean air and water that lasts for generations. Although green infrastructure is often associated with green storm water management systems, it can be used to address a wide range of systems at a variety of scales.
Green systems can be used for wildlife, which are increasingly threatened by human encroachment and climate change. For example, corridors or greenways allow animals to move through human communities; these have the added benefit of being a beautiful space that people want to live near.
Park systems, urban forests, and constructed wetlands also serve as green infrastructure. Constructed wetlands help communities manage water locally and provide habitats for wildlife.
Moreover, green infrastructure practices at the site-scale are used by smart communities for transportation systems (such as green streets) and green roofs, weaving nature into the built environment.
Research shows us that green infrastructure works. Compared to grey infrastructure, green systems are more cost-effective and far more beneficial to people and the environment.

Save
Soil Structure for Green Roof Media Green roofs or living roofs have become popular over the years. This is because they provide ecological benefits, aesthetic value and creative urban architecture. When designing a green roof, there are several factors to take into consideration. Green roof growing media is an integral part of a functioning green roof system. […]
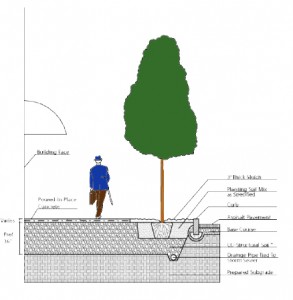 After some experience with gardening and landscaping, you will find that in some cases, standard soil just won’t do. You may need to provide a better, more solid base for large plants such as trees and bushes to grow successfully. This is where knowing about structural soil will help.
After some experience with gardening and landscaping, you will find that in some cases, standard soil just won’t do. You may need to provide a better, more solid base for large plants such as trees and bushes to grow successfully. This is where knowing about structural soil will help.
Structural soil contains larger solid particles and provides more structure that normal soil. These added solid particles create a firm structural base while allowing plant and tree roots to weave around the soil pockets. Structural soil is comprised of a mixture of gap-graded gravels, which are typically made from crushed stone, a hydrogen stabilizing agent and clay loam. This type of soil is perfect when planning to plant trees, especially beside pavement sidewalks or roadways.
Changing Landscaping
Can you picture walking on a beautifully, manicured concrete walkway? Most likely you picture a tree beside this walkway that helps to shape this beautiful image. Structural engineers more often than not will focus on the construction of the concrete walkway or the surrounding road, neglecting the need for a green environment. For this reason, landscape designers are quite important, as they know to choose the right soil for the right result.
By working together with structural engineers, landscape designers are able to successfully grow trees in paved areas. This is normally a challenge due to inadequate soil volume, which is a major requirement for root growth. Soils found under the pavement are usually very compacted, which is the reason why they are unable to support root growth. Only a few trees grow under pavement and when they do, they grow very poorly, dying eventually. It is also worth noting that with the wrong soil the pavement ends up being affected by the root growth. That is why there is need for use of structural soil.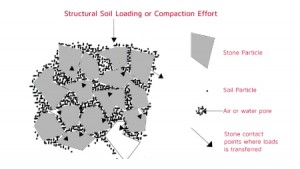
Best Places for Structural Soil
Structural soil has become the best solution for tree-growing in urban settings. This type of soil has been proven to improve tree growth in paved areas, therefore it is the best way to promote street tree planting. Structural soil is used to provide a solid base, which is meant to support masses and at the same time allow for the growth of roots. The result is a perfect crack-free pavement, with a healthy tree growing as expected.
Not all structural soils are the same. They come in different specifications, which are suited for various weather conditions. All the elements that make up structural soil are mixed together. The mix retains a void to allow for water and air movement and gives room for root growth. When used properly, structural soil can allow deep penetration of roots so as to avoid surface heating, which often affects growing trees. Encouraging deep penetration of roots is also good to allow the roots to find sufficient water, necessary for tree growth. This is a great benefit since trees whose roots grow deeply are less likely to lift and crack pavements, leaving you with a great looking pavement and an amazing green environment.
 Both structural engineers and landscapers benefit from the use of structural oil. Engineers appreciate a firm foundation for the pavement and landscapers realize trees with sufficient root volume, air and water for growing trees. Structural soil is becoming more recognized in urban settings as it provides an excellent solution for the people within these areas. It satisfies the need to enjoy good roads and a perfect environment at the same time. It is a lasting solution for both structural engineers and landscapers.
Both structural engineers and landscapers benefit from the use of structural oil. Engineers appreciate a firm foundation for the pavement and landscapers realize trees with sufficient root volume, air and water for growing trees. Structural soil is becoming more recognized in urban settings as it provides an excellent solution for the people within these areas. It satisfies the need to enjoy good roads and a perfect environment at the same time. It is a lasting solution for both structural engineers and landscapers.
Save
 Sustainable Development Goals – Goals for Green Developers
Sustainable Development Goals – Goals for Green Developers
Protecting the natural environment can be a tricky situation especially when you consider human development. At times, the environment works against itself causing health problems for humans, but this is where sustainable development comes in. There has to be a balance between the two in order for this concept to work for future needs. Here are some Sustainable Development projects that work with the environment in a safe, collaborative way.
1. Eco-friendly construction
Eco-friendly construction involves building projects that are not harmful to the environment. In addition to that, the construction project makes efficient use of the available resources. This means that the projects are environmentally friendly and ecologically responsible in planning and actual construction.
This kind of construction, also called green building, is based on the premise that construction in most cases is hazardous in terms of the energy used, distance products have to travel to be used onsite and the environmental impact on the inhabitants and the ecosystem. The following are some of the examples of such construction;
In green building technology, the focus is usually on the conservation of the environment while at the same time preserving human life. The buildings are designed with bio-architecture technology that minimizes health hazard to humans and creates a balance in sustainable development.

2. Eco-friendly water conservation
Water conservation is one of the sustainable development projects that works well to protect both the environment and human life. Instead of using chemical substances to clean and treat water, there is use of biological waste water treatment and re-use that are non-harmful. For example, constructing an aquatic plant-based system that easily enables microorganisms to digest sewage systems and clean greywater. They can enable residents to have clean water for household use and farming. Secondly, rainwater can also be collected, recycled and used in farming and residential settings. Eco-friendly water conservation is based on the sustainability framework to minimize water wastage and provide clean water for human beings.
3. Use of renewable energy
Renewable energy being one of the Sustainable Development Goals has led to projects that reduce the emission of carbon dioxide and hence reducing the impact of global warming. Renewable energy projects are geared towards having clean, reliable and affordable electricity for both commercial and household use. The affordability of these projects allows rural communities, especially in developing countries to have access to electricity and hence improve their lifestyles.
The use of solar energy, for example, is eco-friendly and thus protects both human life and the environment. Solar energy can be used in households and factories. This helps in creating a green environment by avoiding harmful sources of energy.
In as much as protecting the natural environment and protecting human life poses a challenge on how to create the balance, there are some interventions that can be made enhance sustainable development. Indeed, sustainable development is a collective responsibility that requires everyone’s effort to make the world a suitable home for the present and future generations.
Save
